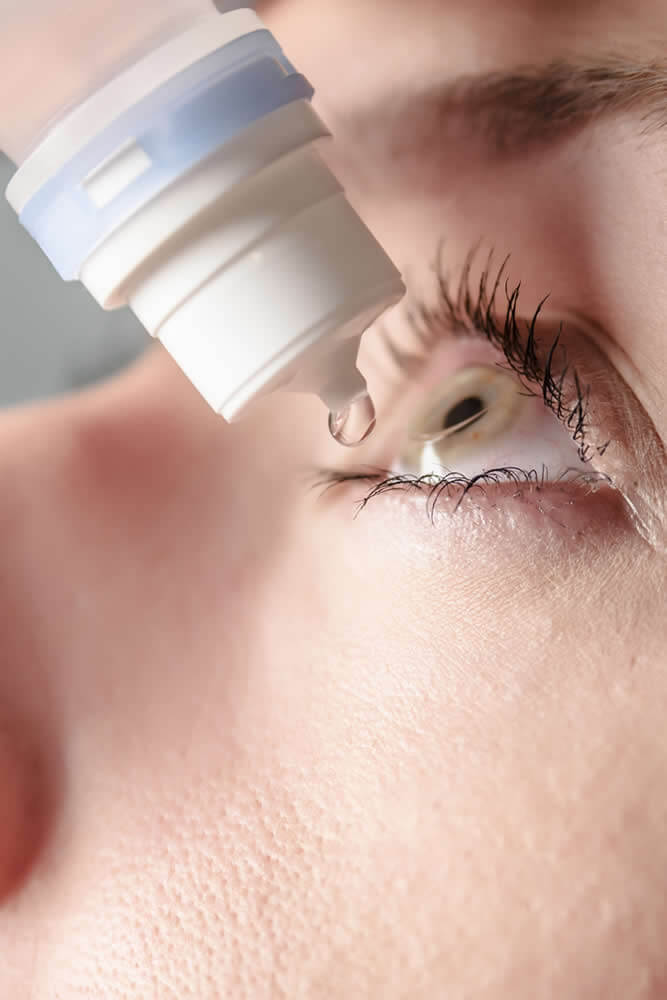
- Why FOCUS for USP <51>?
- P. aeruginosa: Gram negative aerobic rods common in water and soil.
- E.coli: Gram negative facultative anaerobic rods found in fecal contamination.
- S. aureus: Gram positive cocci, found on skin and in nares.
- C. albicans: Yeast, found in mouth and on skin.
- A. brasiliensis: Ubiquitous environmental fungus.
FOCUS Laboratories routinely tests multidose aqueous products for preservative effectiveness. We recognize the long incubation periods involved in these tests, so we set samples up almost as soon as they are received. And our pricing includes full neutralization and toxicity suitability testing, there are no hidden or surprise fees. We are proud to produce accurate, on time and cost effective results.
Call us at 610-866-7272 for a free quote.
Multidose aqueous products such as injectables, eye drops, and cough syrups are formulated with preservatives to prevent spoilage from organisms that may be introduced by the consumer. Microbial contamination introduced by the consumer post manufacture could lead to illness at worse and degradation of potency or product functionality at best.
Preservatives are considered an active pharmaceutical ingredient and the “potency” or quantity in a formulation are usually confirmed by HPLC methods before product release and during stability studies. However, confirming the quantity of preservative by chemical means does not necessarily correlate that the antimicrobial activity of that formulation is still effective. For this reason, USP <51> is performed during formulation and stability trials.
Aliquots of product are inoculated with test species representing broad microbial groups:
Fresh cultures of these test species are introduced to individual aliquots of product at an initial level approximating 1,000,000 cfu/mL. The contaminated product is tested at weekly intervals, and if the preservative is appropriate, the test species will decrease in counts as indicated below.
.
Category |
Products |
7 day |
14 day |
28 day |
1 |
Injections and other parenterals |
Bacteria: >1.0 log reduction from initial |
Bacteria: >3.0 log reduction from initial |
Bacteria: No increase from Day 14 |
Fungus: No increase from initial |
Fungus: No increase from initial |
Fungus: No increase from initial |
||
2 |
Topicals, nonsterile nasals products, and those applied to mucous membranes. |
|
Bacteria: >2.0 log reduction from initial |
Bacteria: No increase from Day 14 |
|
Fungus: No increase from initial |
Fungus: No increase from initial |
||
3 |
Oral aqueous products (non-antacids) |
|
>1.0 log reduction from initial |
Bacteria : No increase from Day 14 |
|
Fungus: No increase from initial count |
Fungus: No increase from initial count. |
||
4 |
Antacids |
|
Bacteria: No increase from initial count |
Bacteria: No increase from initial count |
|
Fungi: No increase from initial count |
Fungi: No increase from initial count. |
USP <51> Antimicrobial Preservative Effectiveness testing also requires validation – in other words neutralizers which are added to the broth or agar to inactivate the preservatives in the formulation, allowing microbes to grow to visible colony forming units in the agar, must be shown to be efficacious. Polysorbate and lecithin are typical neutralizers added to media for organic preservatives such as sorbates and parabens. Halogens may require the addition of sodium thiosulfate. Regardless, neutralization efficacy is demonstrated by spiking product media mixture with <100 cfu test species, and show 50 – 200% recovery.
Test Requirements:
120 gm or mL of product is ideal for USP <51>. Total turn around time is 5 – 6 weeks.